Foot Pain Accessory Navicular Bone
Overview
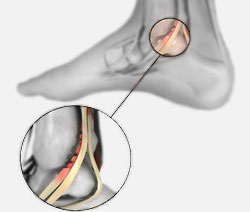
An accessory navicular bone is an accessory bone of the foot that occasionally develops abnormally causing a plantar medial enlargement of the navicular. The accssory navicular bone presents as a sesamoid in the posterior tibial tendon, in articulation with the navicular or as an enlargment of the navicular. Navicular (boat shaped) is an intermediate tarsal bone on the medial side of the foot. It is located on the medial side of the foot, and articulates proximally with the talus. Distally it articulates with the three cuneiform bones. In some cases it articulates laterally with the cuboid. The tibialis posterior inserts to the os naviculare. The tibialis posterior muscle also contracts to produce inversion of the foot and assists in the plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle. Tibialis posterior also has a major role in supporting the medial arch of the foot. This supports is compromised by abnormal insertion of the tendon into the accessory navicular bone when present. This lead to loss of suspension of tibialis posterior tendon and may cause peroneal spastic pes planus or simple pes planus. But, yet a cause and effect relationship between the accessory navicular and pes planus is doubtful and is yet unproved clearly.

Causes
People who have an accessory navicular often are unaware of the condition if it causes no problems. However, some people with this extra bone develop a painful condition known as accessory navicular syndrome when the bone and/or posterior tibial tendon are aggravated. This can result from any of the following. Trauma, as in a foot or ankle sprain. Chronic irritation from shoes or other footwear rubbing against the extra bone. Excessive activity or overuse.
Symptoms
The symptoms of accessory navicular syndrome commonly arise during adolescence, when bones are maturing and cartilage fuses into bone. In other instances, symptoms do not appAccessory Navicularear until adulthood. The signs and symptoms include a visible bony prominence on the midfoot the inner side of the foot above the arch. Redness or swelling of the bony prominence. Indistinct pain or throbbing in the midfoot and arch during or after physical activity.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will diagnose an accessory navicular by examining your child?s foot. Your physician may also obtain x-rays to confirm the accessory navicular and to rule out other conditions.
Non Surgical Treatment
Most children?s symptoms are improved or resolved by taking a break from activities that irritate their feet. Shoe inserts that pad the accessory navicular area are also helpful. If your child?s symptoms do not improve, your physician may recommend a below-the-knee cast or walking boot. Surgery is rarely needed.
Surgical Treatment
Once the navicular inflammation has lessened it is not necessary to perform surgery unless the foot becomes progressively flatter or continues to be painful. For these children, surgery can completely correct the problem by removing the accessory navicular bone and tightening up the posterior tibial tendon that attaches to the navicular bone. The strength of this tendon is integral to the success of this surgery as well as the arch of the foot. Following surgery the child is able to begin walking on the foot (in a cast) at approximately two weeks. The cast is worn for an additional four weeks. A small soft ankle support brace is then put into the shoe and worn with activities and exercise for a further two months.
An accessory navicular bone is an accessory bone of the foot that occasionally develops abnormally causing a plantar medial enlargement of the navicular. The accssory navicular bone presents as a sesamoid in the posterior tibial tendon, in articulation with the navicular or as an enlargment of the navicular. Navicular (boat shaped) is an intermediate tarsal bone on the medial side of the foot. It is located on the medial side of the foot, and articulates proximally with the talus. Distally it articulates with the three cuneiform bones. In some cases it articulates laterally with the cuboid. The tibialis posterior inserts to the os naviculare. The tibialis posterior muscle also contracts to produce inversion of the foot and assists in the plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle. Tibialis posterior also has a major role in supporting the medial arch of the foot. This supports is compromised by abnormal insertion of the tendon into the accessory navicular bone when present. This lead to loss of suspension of tibialis posterior tendon and may cause peroneal spastic pes planus or simple pes planus. But, yet a cause and effect relationship between the accessory navicular and pes planus is doubtful and is yet unproved clearly.

Causes
People who have an accessory navicular often are unaware of the condition if it causes no problems. However, some people with this extra bone develop a painful condition known as accessory navicular syndrome when the bone and/or posterior tibial tendon are aggravated. This can result from any of the following. Trauma, as in a foot or ankle sprain. Chronic irritation from shoes or other footwear rubbing against the extra bone. Excessive activity or overuse.
Symptoms
The symptoms of accessory navicular syndrome commonly arise during adolescence, when bones are maturing and cartilage fuses into bone. In other instances, symptoms do not appAccessory Navicularear until adulthood. The signs and symptoms include a visible bony prominence on the midfoot the inner side of the foot above the arch. Redness or swelling of the bony prominence. Indistinct pain or throbbing in the midfoot and arch during or after physical activity.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will diagnose an accessory navicular by examining your child?s foot. Your physician may also obtain x-rays to confirm the accessory navicular and to rule out other conditions.
Non Surgical Treatment
Most children?s symptoms are improved or resolved by taking a break from activities that irritate their feet. Shoe inserts that pad the accessory navicular area are also helpful. If your child?s symptoms do not improve, your physician may recommend a below-the-knee cast or walking boot. Surgery is rarely needed.

Surgical Treatment
Once the navicular inflammation has lessened it is not necessary to perform surgery unless the foot becomes progressively flatter or continues to be painful. For these children, surgery can completely correct the problem by removing the accessory navicular bone and tightening up the posterior tibial tendon that attaches to the navicular bone. The strength of this tendon is integral to the success of this surgery as well as the arch of the foot. Following surgery the child is able to begin walking on the foot (in a cast) at approximately two weeks. The cast is worn for an additional four weeks. A small soft ankle support brace is then put into the shoe and worn with activities and exercise for a further two months.